Isolated communities are more at risk of rare genetic diseases
The isolation can be geographic or cultural
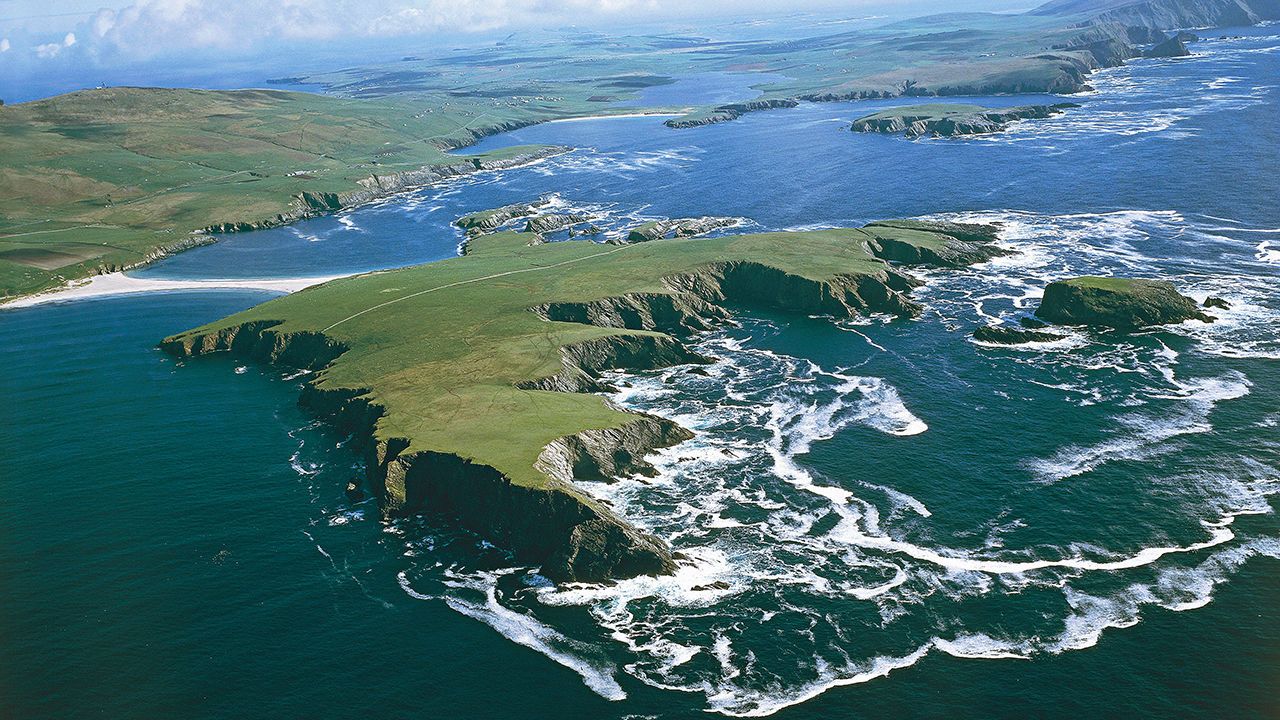

ISLAND LIFE is famously idyllic, but it’s long been known that islanders tend to experience disproportionately high rates of some rare genetically transmitted diseases. Faroe islanders, for example, who live on an archipelago in the North Atlantic Ocean, have a much higher-than-average incidence of carnitine transporter deficiency (CTD), a condition that prevents the body from using certain fats for energy. Inhabitants of Gran Canaria, meanwhile, an island off the north-western coast of Africa, are far more likely than average to have familial hypercholesterolaemia, a condition where the liver cannot process cholesterol effectively.
This article appeared in the Science & technology section of the print edition under the headline “The gene-variant archipelago”
Discover more
AI researchers receive the Nobel prize for physics
The award, to Geoffrey Hinton and John Hopfield, stretches the definition of the field

A Nobel prize for the discovery of micro-RNA
These tiny molecules regulate genes and control how cells develop and behave

AI offers an intriguing new way to diagnose mental-health conditions
Models look for sound patterns undetectable by the human ear
Why it’s so hard to tell which climate policies actually work
Better tools are needed to analyse their effects
An adult fruit fly brain has been mapped—human brains could follow
For now, it is the most sophisticated connectome ever made
Immune therapy shows promise for asthma, heart disease—and even ageing
Making treatment quick and affordable will be the challenge
