A Nobel prize for the discovery of micro-RNA
These tiny molecules regulate genes and control how cells develop and behave
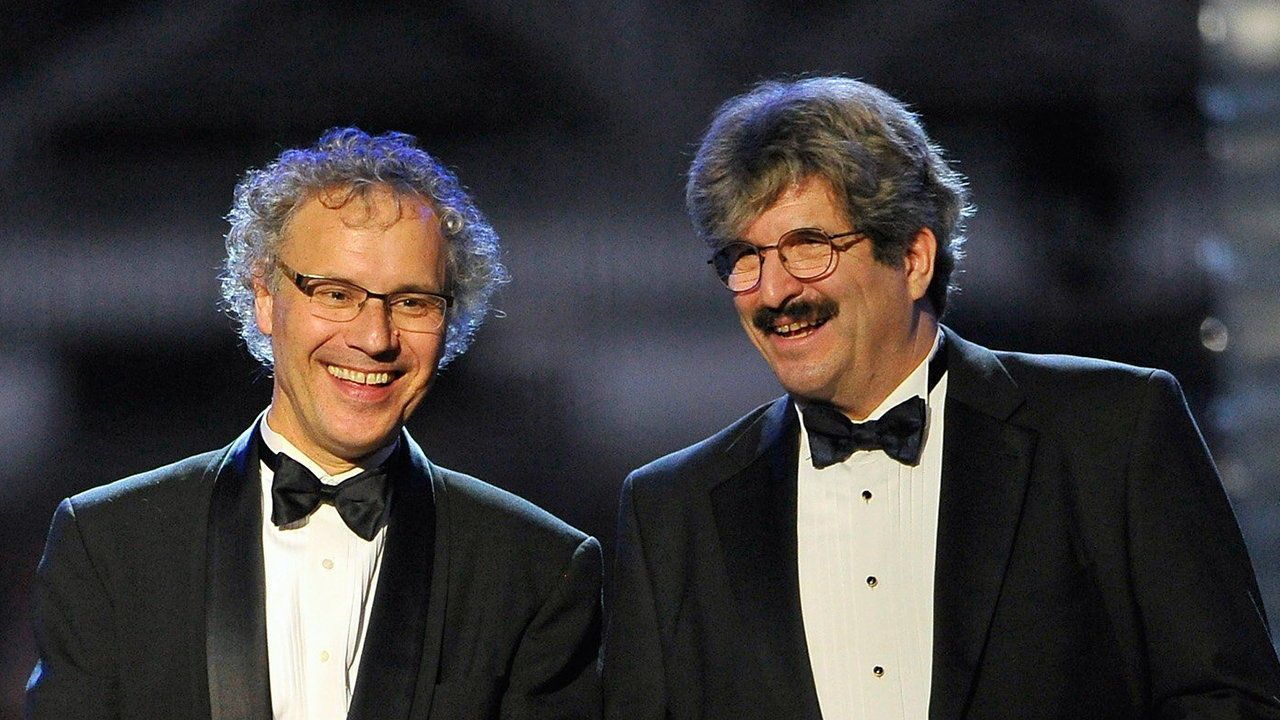

Before the committee that awards the Nobel Prize for physiology or medicine made its announcement on October 7th, the speculation about which discovery would win ranged from the revolution in the treatment of obesity to cancer-causing genes; from understanding the gut microbiome to perhaps even the mapping of the human genome itself—something that has still not earned the coveted “call from Sweden”. The broad trends in what ends up winning the prize are plain: they increasingly recognise the smallest advances at the molecular and cellular level—rather than work on physiology or organs—because that is where the most exciting scientific frontiers are to be found.
Discover more
AI researchers receive the Nobel prize for physics
The award, to Geoffrey Hinton and John Hopfield, stretches the definition of the field

AI offers an intriguing new way to diagnose mental-health conditions
Models look for sound patterns undetectable by the human ear

Why it’s so hard to tell which climate policies actually work
Better tools are needed to analyse their effects
Isolated communities are more at risk of rare genetic diseases
The isolation can be geographic or cultural
An adult fruit fly brain has been mapped—human brains could follow
For now, it is the most sophisticated connectome ever made
Immune therapy shows promise for asthma, heart disease—and even ageing
Making treatment quick and affordable will be the challenge